- 1. What information does TM-MC hold?
- TM-MC provides information on the constituent compounds of medicinal plant materials in Northeast Asian traditional medicine.
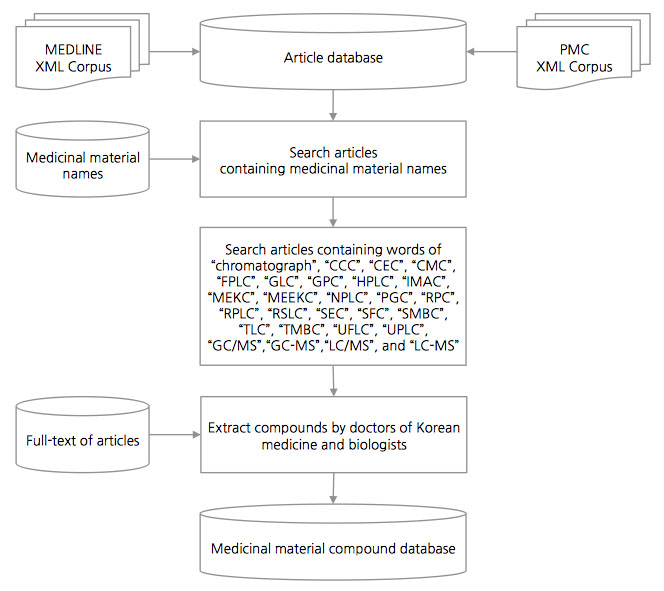
Information on the constituent compounds of these medicinal materials was extracted manually from chromatography articles searched on MEDLINE and PubMed Central. In addition, links to PubMed are also provided to allow users to examine and review the articles from which the information has been extracted.
Users are provided information on the names (Latin name, common name, Korean name, Chinese name, scientific name), photograph, effects, and treatment targets for each medicinal material. In addition, each scientific name is connected to the species on the NCBI Taxonomy and each chemical compound is connected to the chemical compound on PubChem and ChemSpider database, respectively, thus allowing users to see chemical formulas or other information provided by PubChem or ChemSpider database.
- 2. How was TM-MC constructed?
- TM-MC was constructed based on medicinal materials taken from Korean, Chinese, and Japanese pharmacopoeias.
Synonyms of the same medicinal materials in these three pharmacopoeias were distinguished, and papers containing the names of these medicinal materials were searched on the MEDLINE and PubMed Central.
Out of those published studies, papers on chromatography were selected.
Korean medical doctors and biologists then read the abstracts and full texts of all the papers thus selected, manually extracting the constituent compounds of the medicinal materials.
In addition, when the original texts of the papers were located on other websites such as those of the publishers, even those versions were reviewed as well.
Chromatograms were included in some of the articles which extracted compound information related to the medicinal materials in this study. Those that did not involve chromatograms were either in the form of abstracts or cited articles with chromatograms as references. It should be noted that there are some cases when authors use different names for the same compound. If the articles contain the chemical structure or chromatogram, readers can determine whether the two compounds are the same. However, distinguishing between the two compounds can be difficult if the articles make references in name only. In addition, it is not easy to decide which of the names to use in standardization. (E.g. (+)-N-methylpseudoephedrine and (+)-methylpseudoephedrine of the Ephedra herb) Because a basis for standardizing compound names was lacking, the names were retrieved as they were used in existing studies despite the possibility of repetition.
- 3. How does TM-MC differ from other Traditional Medicine databases?
- At the moment, TM-MC is a database of the constituent compounds of medicinal materials in the field of traditional medicine and still does not include information on formulas, diseases, and genes.
However, it is not a database which simply integrates information on the constituent compounds of medicinal materials which can be found in diverse places.
It was constructed by directly searching for and reviewing information in papers from which the constituent compounds of medicinal materials were investigated.
Of course, because TM-MC provides links to the papers from which the constituent compounds of medicinal materials were extracted, users can easily check online.
In the field of traditional medicine, many databases exist that provide the constituent compounds of medicinal materials. These databases provide information on thousands of medicinal materials. However, these numbers result from the fact that these databases have not distinguished synonyms of the same medicinal materials. In fact, the number of medicinal materials in Korean, Chinese and Japanese pharmacopoeias does not exceed 1,000. On the other hand, the TM-MC has distinguished synonyms of medicinal materials.
In addition, many databases are not open to the public. In contrast, TM-MC is open and available to everyone.
- 4. How can I obtain information on the TM-MC?
- Users can see lists of the entire medicinal materials and chemical compounds on the “Browse” menu on the TM-MC website.
All information on TM-MC can be downloaded through the "Download" menu on the TM-MC website. At the moment, information may be downloaded as files in the Web Ontology Language (OWL) and Excel formats.
- 5. How can I search for information on TM-MC?
- In searching for the constituent compounds of medicinal materials, generally two methods are provided.
1. Browse
(For first-time users who do not know what information exists on TM-MC)(1) Users can see lists of all medicinal materials and compounds on the TM-MC by clicking on the "Browse" menu on the TM-MC website.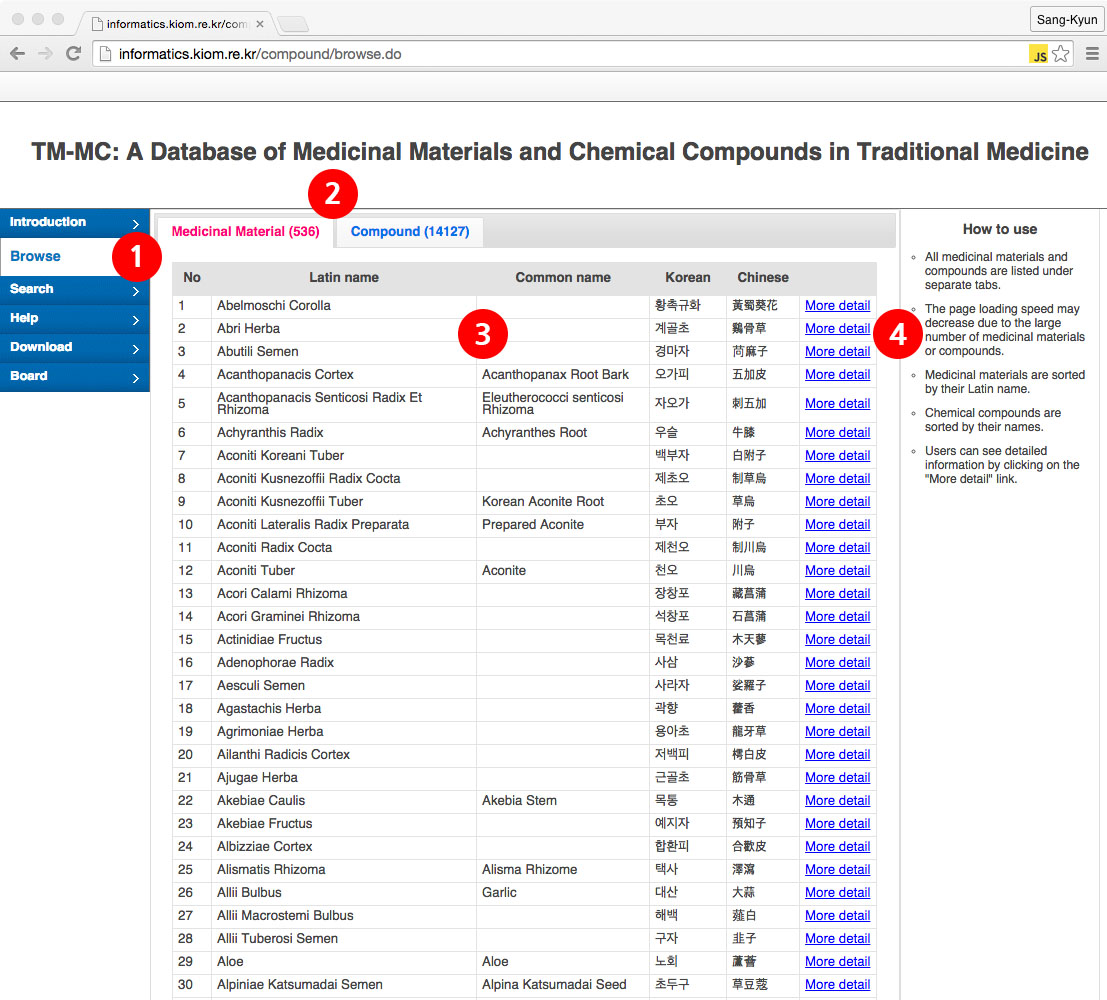
(2) The lists of medicinal materials and chemical compounds are separated by tabs and can be viewed by selecting the respective tabs (search speed may decrease when using the compound tab due to the large number of compounds)
(3) Users can see lists of the Latin names, common names, Korean names, and Chinese names of medicinal materials, which are sorted in an ascending order by their Latin names (in some cases, common names and Chinese names are absent)
(4) Users can see detailed information in a new window, including a photograph, the scientific name, effects, treatment targets, and constituent compounds of each medicinal material, as well as a link to papers from which the medicinal material has been extracted, by clicking on the "More detail" link.
(5) The names of chemical compounds are shown sorted in an ascending order. As for chemical compounds on the PubChem Compound, links are provided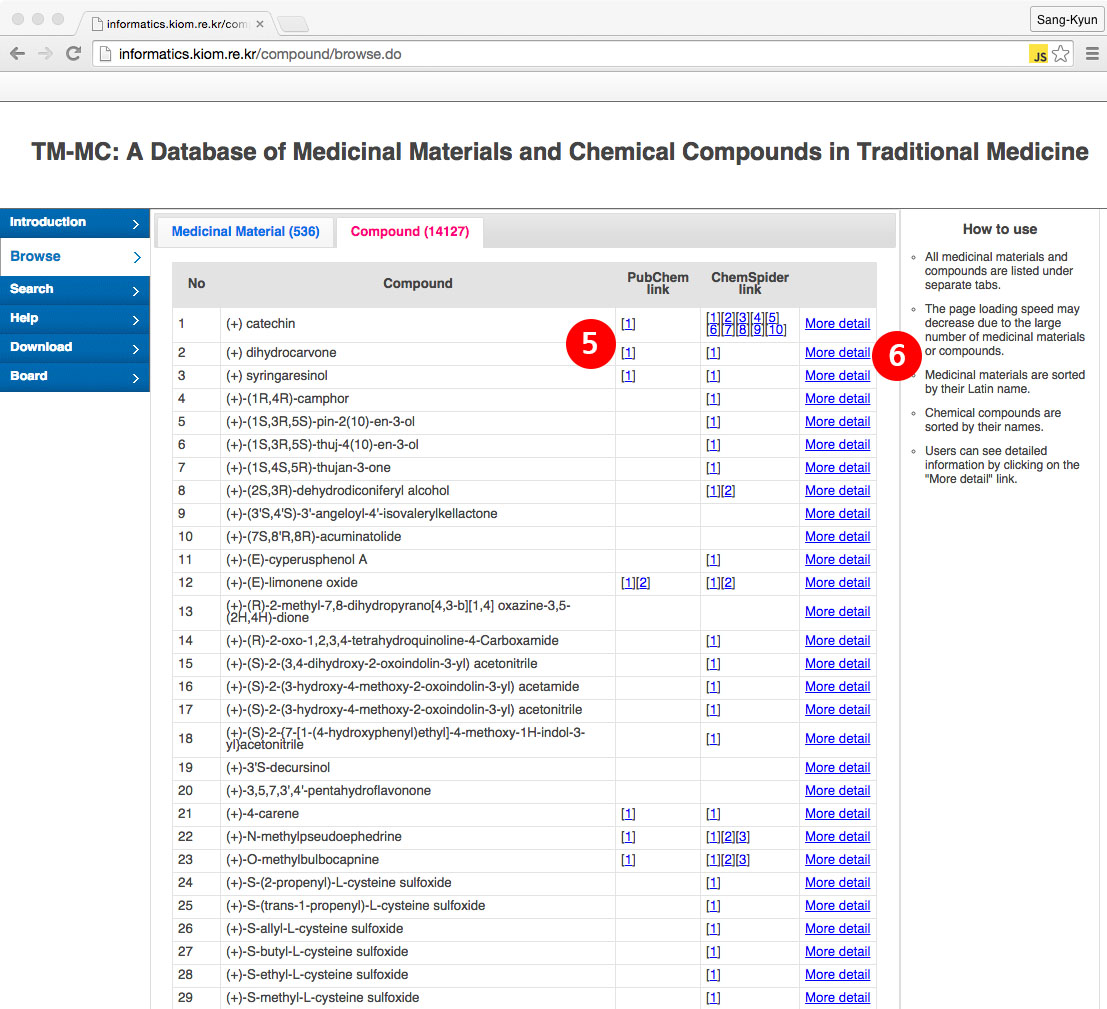
(6) Users can see detailed information in a new window, including a list of medicinal materials having a chemical compound as their constituent compound and links to papers from which the chemical compounds have been extracted, by clicking on the "More detail" link.
2. Keyword search
(For users who know what information exists on TM-MC)(1) The search screen appears when users click on the "Search" menu on the TM-MC website. At the top of the search screen is the search field. When search terms are entered in this search field, a maximum of ten medicinal materials and chemical compounds including the search terms entered are recommended.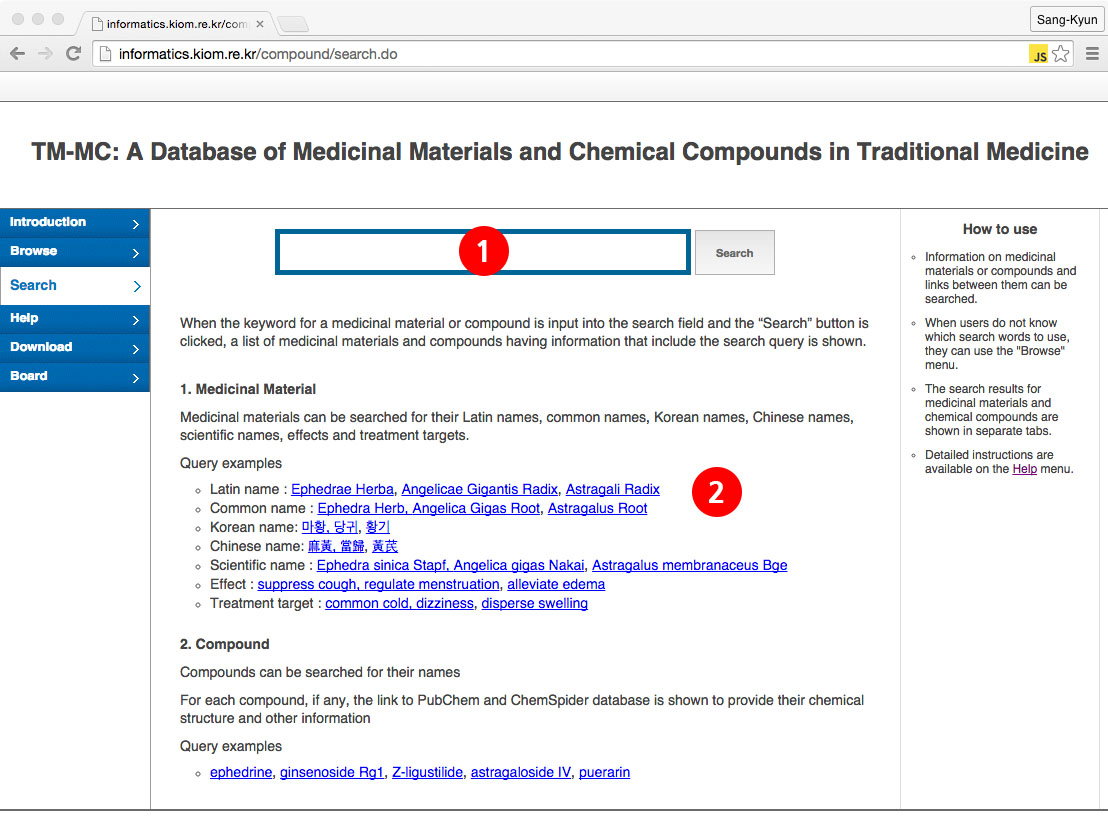
(2) Search examples are shown for users who do not know which search terms to use. When users click on a search example, searches are made using the keyword clicked on.
(3) When users search for "Ephedra herba" in (1) or click on "Ephedra herba" in (2), the search results for "Ephedra herba" are shown.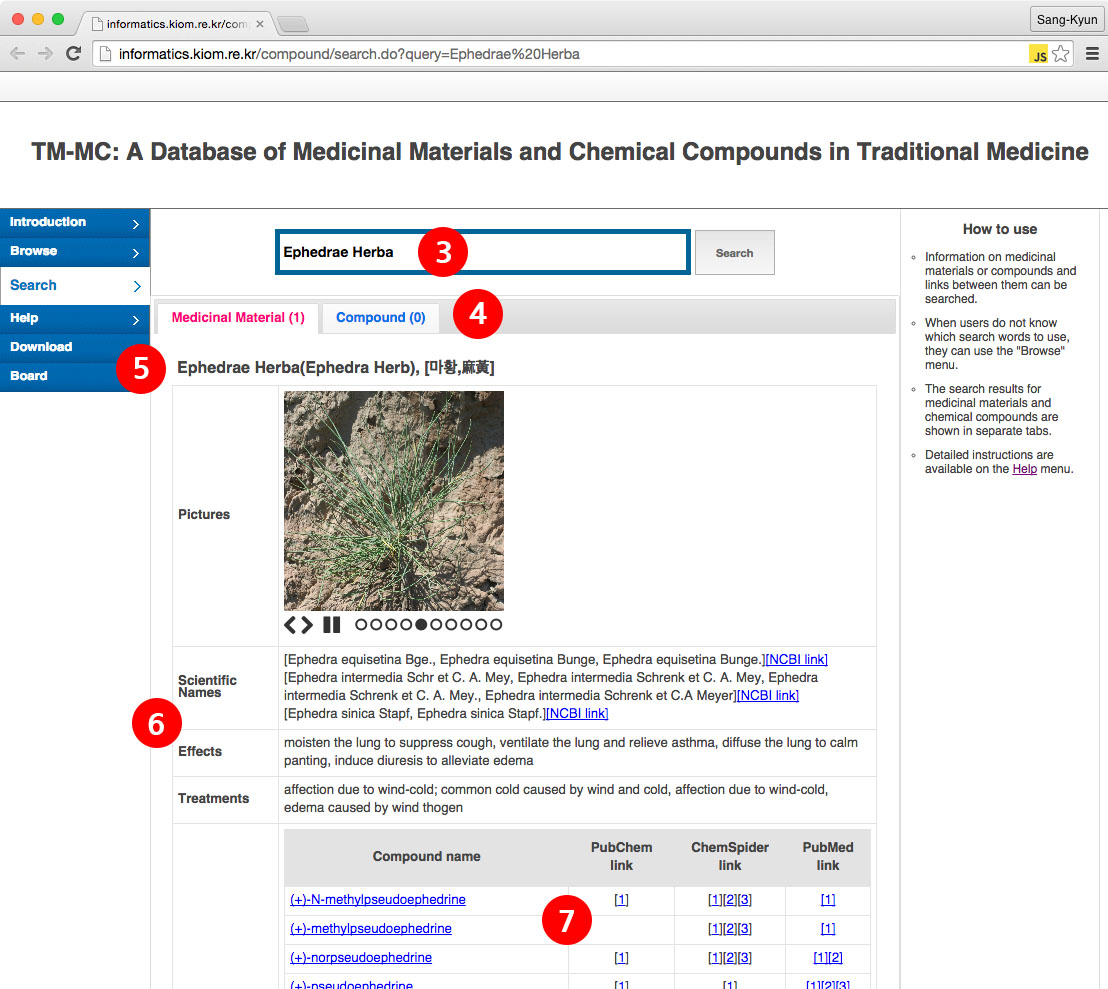
(4) The search results are shown with medicinal materials and compounds separated by tabs. Tabs show the numbers of both medicinal materials and compounds searched for.
(5) The name of each medicinal material is shown in the form of “Latin name (common name), [Korean name, Chinese name].” When many medicinal materials exist for a single search term, only a list of the names of the medicinal materials is shown first. When users click on the name of each medicinal material, the detailed information in (6) is shown.
(6) Detailed information including a photograph, the scientific name, effects, treatments, and constituent compounds of each medicinal material is shown. A link to NCBI Taxonomy exists next to each scientific name.
(7) Links to the names of the constituent compounds of each medicinal material, to the PubChem Compound, and to PubMed articles from which medicinal materials and constituent compounds have been extracted, are shown
(8) When users search for "ginsenoside Rg1" in (1) or click on "ginsenoside Rg1" in (2), the search results for "ginsenoside Rg1" are shown. When a link to the PubChem Compound regarding constituent compounds exists, it is shown as well.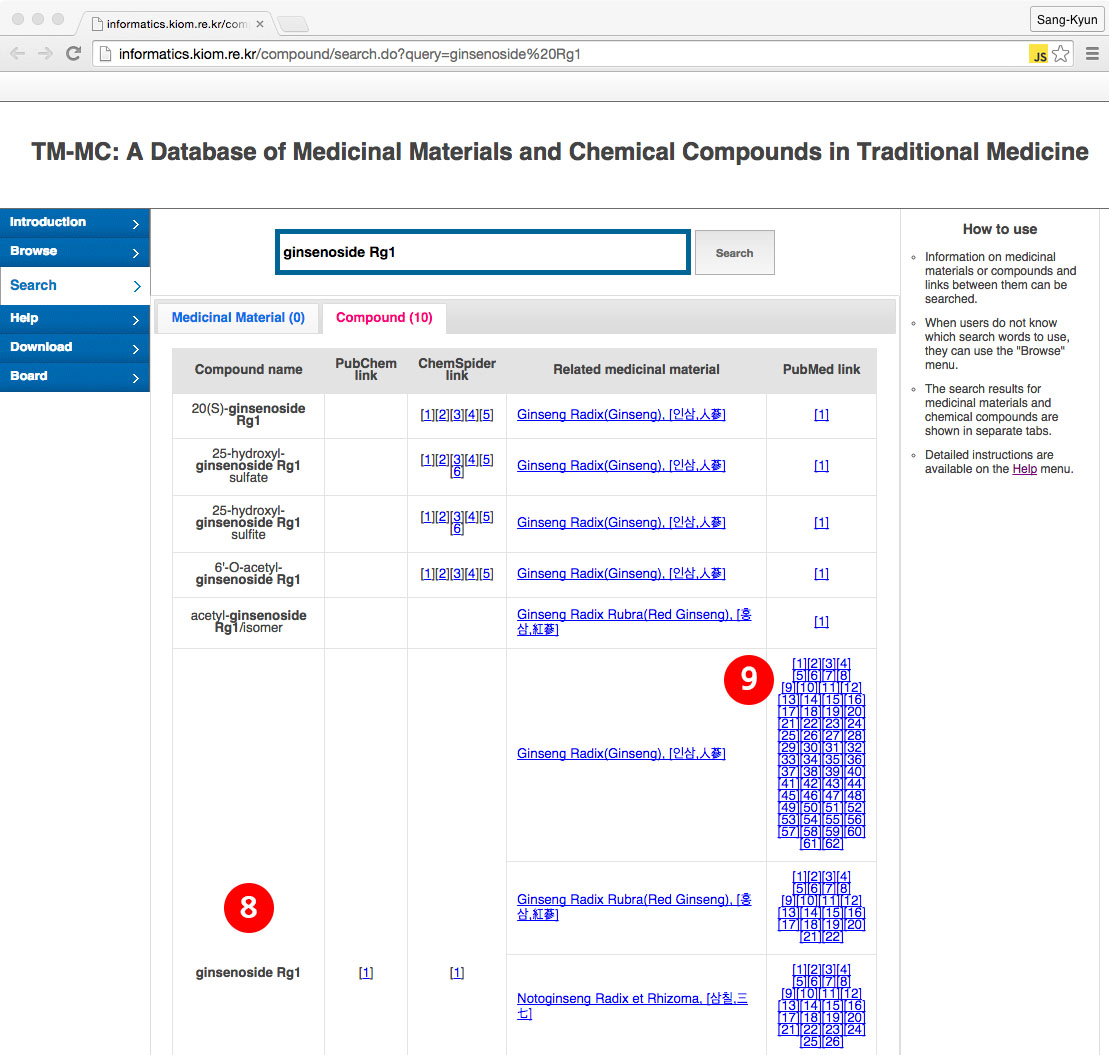
(9) A list of medicinal materials having ginsenoside Rg1 as a constituent compound is shown. In addition, links to PubMed articles from which the medicinal materials and constituent compounds have been extracted are shown as well.
